728x90
상속(Inheritance)
- 상위 클래스의 특성을 하위 클래스에 물려주는 것 (Ex. 자동차 -> 스포츠카 )
- superclass : 특성을 물려주는 상위 클래스
- subclass : 특성을 물려받는 하위클래스
public class Car {
...
}
public class SportsCar extends Car {
...
}
public class Lamborghini extends SportsCar {
...
}자바 상속
- 클래스를 다중 상속 지원하지 않음 (cf. Python)
- 상속 횟수는 무제한
- 최상위 클래스는 java.lang.Object
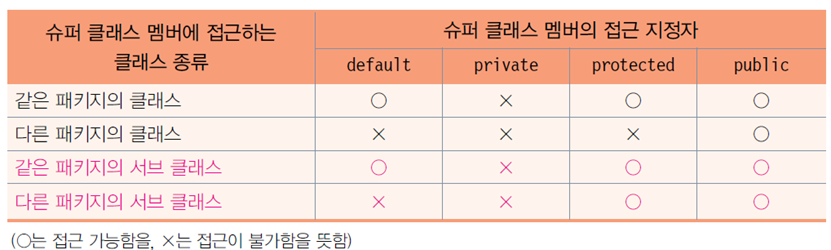
슈퍼 클래스와 서브 클래스
- 서브 클래스의 객체에는 슈퍼 클래스가 멤버가 포함
- 슈퍼 클래스의 private 멤버는 상속되지만 서브 클래스에서 직접 접근 불가
- 슈퍼 클래스 내의 public 또는 protected 메서드를 통해 접근 가능
캐스팅
- 업캐스팅(upcasting) : 서브 클래스의 레퍼런스 값을 슈퍼 클래스 레퍼런스에 대입
- 슈퍼 클래스의 멤버만 접근 가능
- 다운캐스팅(downcasting) : 슈퍼 클래스 레퍼런스를 서브 클래스 레퍼런스에 대입
- 업캐스팅된 것을 다시 원래대로 되돌림
- instanceof
- 업캐스팅된 레퍼런스는 객체의 진짜 타입을 구분하기 어려움
- instanceof 연산자를 통해 객체의 진짜 타입 식별
- true/false로 값 return
class Person {
...
}
class Student extends Person{
...
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Student(); // upcasting
Student s;
s = (Student) p; // downcasting
if (p instanceof Person) // true
if (p instanceof Student) // false
if (s instanceof Person) // false
if (s instanceof Student) // true
}메서드 오버라이딩 (Method Overriding)
- 슈퍼 클래스의 메소드를 서브 클래스에서 재정의
- 메소드 이름, 인자, 타입, 개수, 리턴 타입 등을 모두 동일하게 작성
- static, private, final 메서드는 오버라이딩 불가
class Person {
String name;
...
void info() {
System.out.println("사람 : " + this.name);
}
}
class Student extends Person{
void info() {
System.out.println("학생 : " + this.name); // Overriding
}
}
오버라이딩과 오버로딩을 혼동하지 말자

추상 메소드 (abstract method)
- 선언되어 있으나 구현되어 있지 않은 메서드
- abstract 키워드로 선언 (Ex. public abstract int getValue();)
- 서브 클래스에서 오버라이딩해서 구현
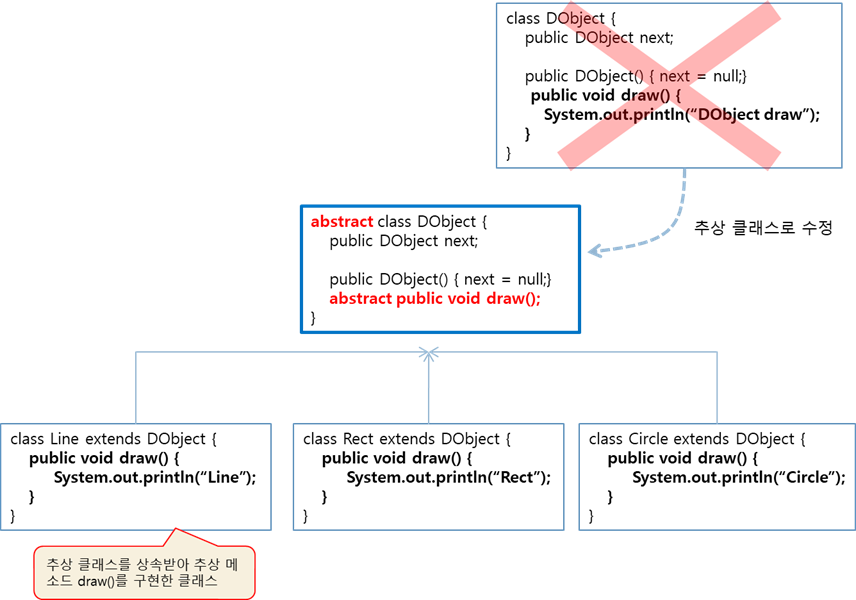
추상 클래스 (abstract class)
- 추상 메서드를 하나라도 가진 가진 클래스 or 클래스 앞에 abstract로 선언한 클래스
- 추상 클래스는 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없다.
abstract class Person {
public String name;
abstract public void walk();
}추상 클래스의 용도
- 설계와 구현 분리
- 서브 클래스마다 목적에 맞게 추상 메소드를 다르게 구현
인터페이스 (inferface)
- 모든 메서드가 추상 메서드인 클래스
- 인터페이스는 상수와 추상 메서드로만 구성, 변수 필드 선언 불가
- 객체 생성 불가, 레퍼런스 변수는 선언 가능
- interface 키워드로 선언 (Ex. public interface Driver{})
public interface Car {
int MAX_SPEED = 300; // static fianl 생략, 상수 필드 선언
int drive(int speed); // abstract public 생략, 추상 메소드 선언
}
new Car(); // Error : inferface는 객체 생성 불가
Car car; // 레퍼펀스 변수는 선언 가능인터페이스 다중 구현
- 인터페이스를 이용하여 다중 상속 구현 가능
inferface USBModule {
void connectUSB();
}
inferface PrintModule{
void setColor();
void printAll();
}
public class PrintDriver implements USBModule, PrintModule {
void connectUSB() {...};
void setColor() {...};
void printAll() {...};
// 추가적으로 다른 메소드 작성 가능
boolean getState() {...}
}
이미지 출처 : 명품 JAVA 프로그래밍 (황기태, 김효수 저)
728x90
'Java > Java 기본' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 네트워크 (0) | 2022.12.26 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 입출력 스트림과 파일 입출력 (0) | 2022.12.26 |
| [JAVA] 제네릭과 컬렉션 (0) | 2022.12.26 |